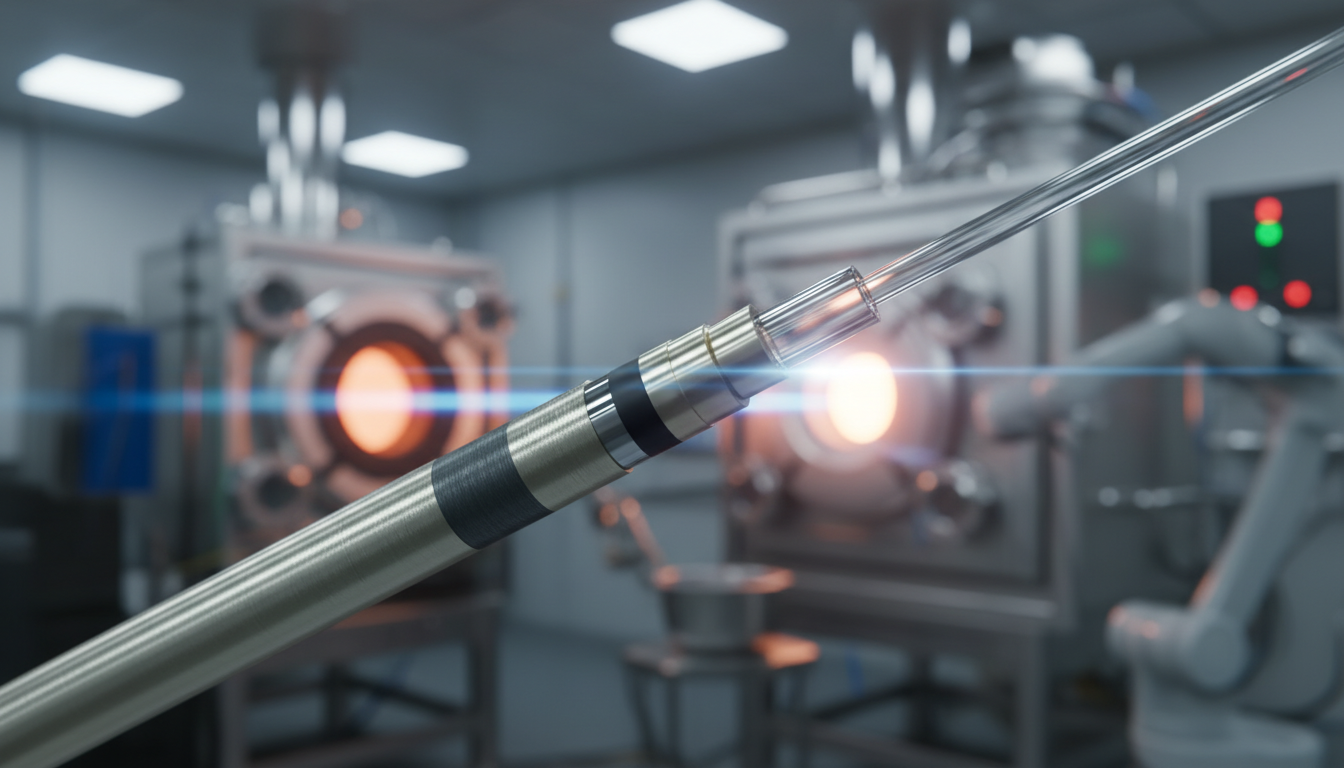
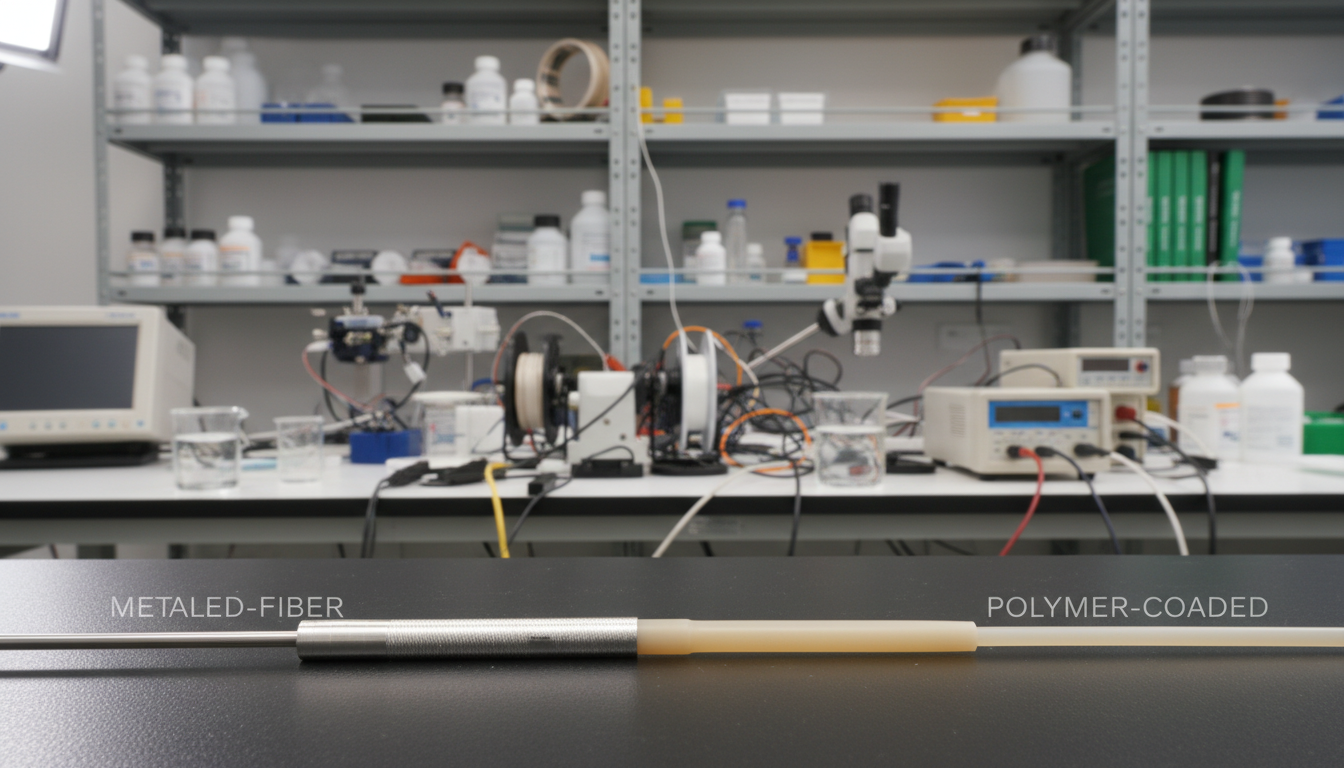
Metal coated fiber is a game-changer when regular materials can’t handle the heat. NASA and Boeing use it for parts that get hotter than 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit. It’s made of flexible fiber cores wrapped in metal, keeping them strong even when plastics melt.
This material is a big leap in science for extreme conditions. Corning and Thorlabs have made fibers that stay strong in space’s harsh conditions. They don’t let out gas and keep signals clear, even in near-vacuum.
The metal layer is key. It protects the fiber from heat and vacuum. This lets the fiber send light or signals without damage. Now, industries like semiconductors and oil use these fibers for their tough jobs.
Key Takeaways
- Metal coated fiber withstands temperatures above 1,000°F while maintaining performance
- The metal coating prevents outgassing in vacuum chambers and space applications
- These fibers combine flexibility with exceptional heat and environmental resistance
- Aerospace giants like NASA and Boeing use them for critical spacecraft components
- Vacuum-compatible materials maintain signal integrity at near-zero air pressure
- Metal coatings protect fiber cores from direct exposure to harsh conditions
- Industries from semiconductors to oil exploration rely on these extreme environment solutions
Understanding Metal Coated Fiber and Its Composition
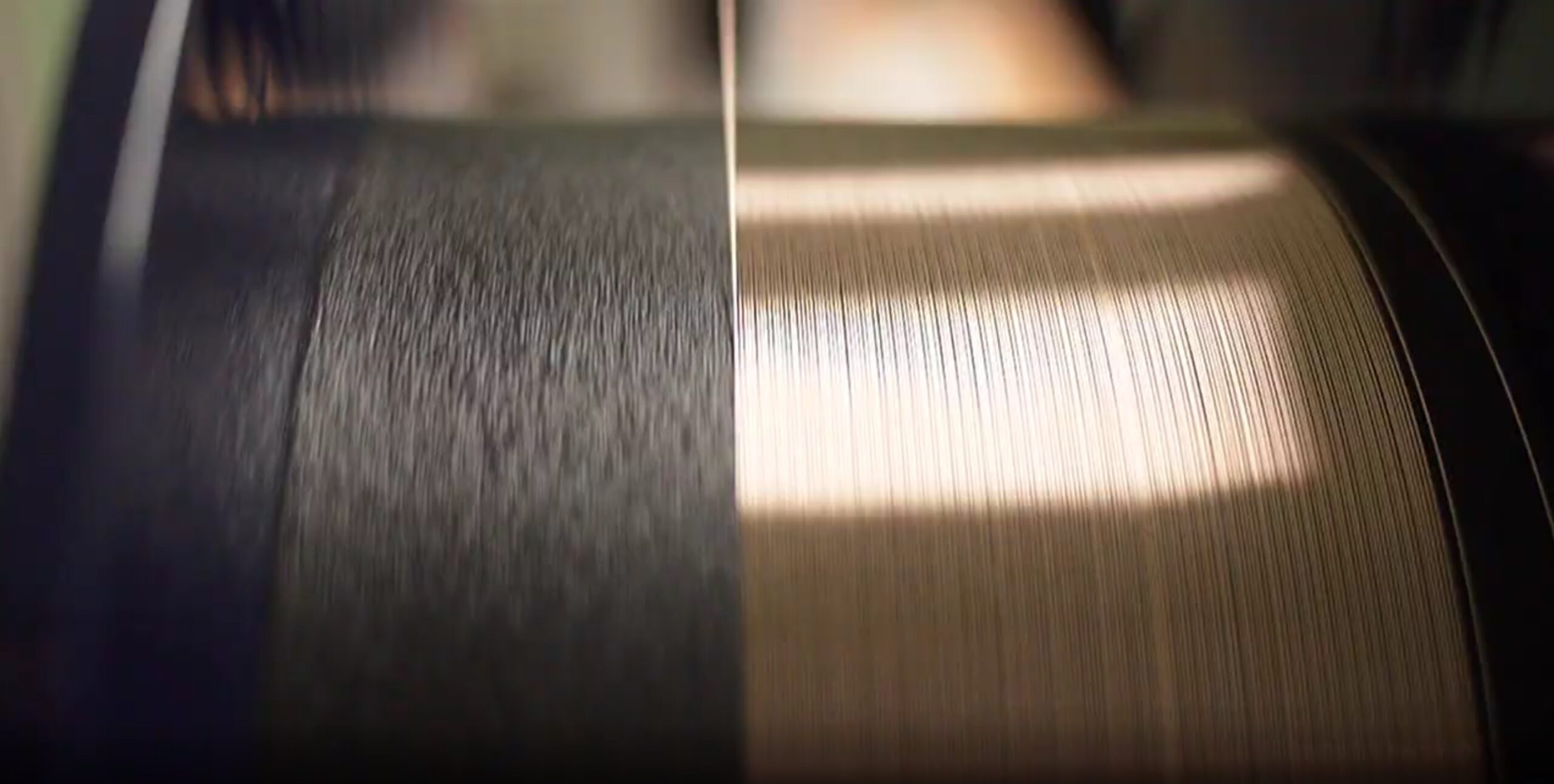
Metal coated optical fiber is a cutting-edge technology. It combines the light-guiding abilities of traditional fibers with added durability. The core is made of glass or silica, which carries light signals. Then, protective metal layers are added, boosting the fiber’s performance.
The choice of coating materials is key to the fiber’s performance. Each metal has its own strengths for various uses and settings. These metal layers also create an electrical path while keeping the fiber’s optical properties intact.
| Metal Type | Temperature Range (°F) | Key Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | -320 to 750 | Lightweight, cost-effective | Aerospace sensors |
| Gold | -420 to 1300 | Corrosion resistance | Medical devices |
| Copper | -200 to 850 | Excellent conductivity | Industrial monitoring |
| Nickel | -300 to 1100 | Magnetic shielding | Nuclear facilities |
The making of metal coated fiber ensures uniform thickness throughout. This uniformity is vital for reliable shielding against electromagnetic interference and thermal protection. The metal coating allows for charge transport while keeping the fiber flexible and good at transmitting light.
Applications of Metal Coated Fiber in High-Temperature Environments
Metal coated fibers are great for extreme conditions where normal materials can’t handle it. They are high temperature fiber solutions that keep important parts working well, even when it’s very hot.
In aerospace applications, these fibers are key for space and air travel. NASA uses them in satellites that go from -250°F to 250°F in space. Boeing and Airbus use them in jet engines that get up to 1,800°F.
The car industry also needs automotive heat resistance from metal coated fibers. They are used in:
- Exhaust system sensors that check temperatures up to 1,600°F
- Engine control units that need to stay cool
- Catalytic converter monitoring systems
- Turbocharger temperature sensors in fast cars
Industrial temperature solutions with metal coated fibers are used in factories. Steel plants use them in blast furnace monitoring at 3,000°F. Chemical plants use them in reactors and distillation columns. Power plants use them in gas turbines and boilers.
These fibers can handle lots of heat without breaking down. Normal plastics would melt or break down fast. But metal coated fibers work well for years, saving money and avoiding breakdowns.
The Role of Metal Coated Fiber in Vacuum Environments
Metal coated fibers are key in vacuum settings where regular materials fail. They are vital in fields like semiconductor making and aerospace studies. Their special features are needed to keep vacuum chambers clean and stable.
These fibers stand out because they resist outgassing well. Normal fibers release gases in a vacuum, harming equipment and messing up measurements. But metal coated fibers block these gases, keeping things clean.
Companies like Intel and TSMC use these fibers in their high-tech equipment. The metal coating keeps the fibers stable even in very low pressure. This is important for keeping precise measurements in chip making.
In space, these fibers are also very useful. NASA and SpaceX use them in:
- Satellite communication systems
- Thermal insulation blankets
- Vacuum testing chambers
- Space simulation equipment
Places all over the world count on these fibers for their research. They keep instruments and samples safe in vacuum setups. This makes them great for long-term use where changing them is hard or expensive.
Key Advantages of Metal Coated Fiber
Metal coated fibers have amazing thermal resistance benefits. They can handle extreme temperatures better than regular fibers. The metal coating protects them, allowing use up to 600°F without losing performance.
These fibers also have great electrical conductivity. They help control static charges and provide grounding paths in sensitive equipment. The main electrical benefits are:
- EMI shielding for electronic components
- Adjustable volume and surface resistivity
- Static discharge prevention in volatile environments
- Signal transmission capabilities in smart textiles
These fibers are also great for harsh environments. The metal layer keeps the core fiber safe from moisture, chemicals, and oxidation. This makes them last longer in places like the sea, space, and factories.
Engineers can adjust the coating thickness for different needs. Aluminum coatings are light and protective, while copper is better for conductivity. Nickel is best in corrosive areas. Each metal has its own benefits for various industries.
It’s important to manage Joule heating at connections. Good design keeps the fiber’s conductivity steady. This ensures it works well in situations where failure is not acceptable.
Comparing Metal Coated Fibers to Traditional Fibers
When you look at metal coated fibers and traditional ones, the performance comparison shows big differences. Standard fibers are okay for simple tasks but can’t handle tough conditions. Metal coated fibers, on the other hand, can handle extreme situations where others fail.
The traditional fiber limitations are clear in tough environments. Regular fibers don’t conduct electricity well, which is a big problem for many industrial uses. They also break down at high temperatures and don’t do well in vacuum conditions. Metal coated fibers, though, can handle up to 1,800°F and stay strong in extreme vacuum conditions.
| Feature | Traditional Fibers | Metal Coated Fibers |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | 300-500°F | 1,200-1,800°F |
| Electrical Conductivity | Poor to None | Excellent |
| Vacuum Compatibility | Limited | Superior |
| Service Life | 2-3 years | 8-10 years |
The long-term cost analysis shows metal coated fibers are a better deal, even if they cost more upfront. A standard fiber system might start at $5,000 but needs to be replaced every three years. Metal coated fiber systems cost $12,000 but last ten years with little upkeep. Over ten years, you save thousands and avoid expensive equipment failures.
Metal coatings give uniform electrical properties in all directions. This makes designing systems easier than with carbon-filled alternatives that only conduct in specific directions. The consistent performance cuts down on engineering complexity and boosts reliability in many applications.
Innovations in Metal Coating Technologies
The metal coating industry has seen big changes in recent years. Now, computer-controlled processes help make coatings with exact thickness. These systems watch and adjust the coating as it’s applied, making sure each fiber gets the right amount of metal.
New ways to bond metals with fibers have come along. Atomic layer deposition and plasma-enhanced coating make the bond stronger. This has cut down on coating defects. Companies like Applied Materials and Lam Research have made systems that apply multiple metal layers at once, making the coatings better.
New materials for coatings are being tested. Scientists are mixing aluminum, copper, and nickel to make coatings that work better in certain situations. They’ve also found a way to control how much metal is needed for electrical conductivity, saving weight and cost.
Checking the quality of coatings has gotten much better. New scanning systems can spot tiny problems that could affect how well the coating works. Tools like laser interferometry and electron microscopy give feedback right away. These advances mean every meter of coated fiber meets high standards. Artificial intelligence is even being used to predict and stop problems before they start, taking metal coated fibers to new heights.
Choosing the Right Metal Coated Fiber for Your Needs
Choosing the right metal coated fiber is all about knowing your application requirements. First, think about where the fiber will be used. Different coatings like aluminum, gold, or copper handle acids, bases, and solvents differently. Also, the temperature matters a lot—aluminum works up to 400°C, and gold goes beyond 700°C.
When picking a fiber, don’t forget about contact resistance. This is often more important than the fiber’s overall conductivity. The quality of the surface finish and how much pressure is applied also affect how well it works. Plus, changes in temperature can cause the fiber to expand and contract, which might damage connections over time.
Following the right guidelines is key to avoiding mistakes. Here are some important things to consider:
- Operating temperature range and thermal cycling frequency
- Chemical exposure types and concentration levels
- Required bend radius and mechanical stress points
- Electrical conductivity needs versus signal integrity
- Environmental sealing requirements
Manufacturing methods can also impact the fiber’s performance. For example, injection molding can create fibers with different electrical properties on the surface and inside. Knowing these differences is essential for reliable performance in your application.
Maintenance and Care for Metal Coated Fiber Products

Metal coated fibers need regular care to work well in tough settings. Simple steps can make them last longer and avoid expensive breakdowns. Start by checking your fiber cables monthly for wear at connections and bends.
Important care tips include:
- Look for scratches or coating chips on fiber ends during checks
- Clean connectors with isopropyl alcohol and Kimtech wipes
- Keep unused fibers in protective cases at room temperature
- Support long cables every 3 feet to avoid sagging
Temperature changes can cause metal coatings to expand and contract differently than glass cores. This stress can lead to micro-cracks over time. Use a standard multimeter to check resistance values during use. A sudden increase in resistance often means coating damage before it fails completely.
Common fixes can solve problems fast. If signal strength drops, first check the connector surfaces. Dirt and residue can block light. When fibers are near vibrating equipment, add clamps to reduce stress.
Keep a log of cleaning dates and resistance readings. This helps spot issues before they get worse. Replace fibers with resistance changes over 15% from baseline. With the right care, metal coated fibers from Fiberguide Industries can last 5-10 years in industrial use.
Conclusion: The Future of Metal Coated Fiber
Metal coated fiber is on the brink of huge market opportunities. Demand from big names like Intel and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company is driving it forward. Companies like First Solar and SunPower need it for solar panels. SpaceX and Boeing also use it for their advanced spacecraft.
Environmental rules are pushing industries to use safer, more efficient protection. Metal coated fibers meet these standards and open new areas for use. They have the same electrical and thermal properties but are much lighter. Companies like Corning and AFL Telecommunications are working to make these fibers work seamlessly in systems.
The future brings multi-functional coatings that do many things at once. Researchers are making coatings that resist heat, conduct electricity, and block chemicals. This will lead to new uses in medical devices, electric cars, and quantum computing. As costs go down and performance gets better, metal coated fiber will take over many industrial uses in America.
FAQ
What exactly is a metal coated optical fiber and how does it differ from standard fiber?
A metal coated optical fiber has a core surrounded by metals like aluminum or gold. It’s different from standard fibers because it has a metal coating. This coating protects the fiber from extreme temperatures and electrical damage.
It’s perfect for places like aerospace and high-temperature industries. The metal coating keeps the fiber working well in harsh conditions.
What temperatures can high temperature fiber with metal coatings withstand?
High temperature fiber can handle temperatures up to 700°C. This is much higher than standard fibers. Gold-coated fibers work best at the highest temperatures.
Aluminum and copper coatings are good for lower temperatures. These fibers stay strong even when they get very hot.
Why is vacuum compatible fiber essential for semiconductor manufacturing?
Vacuum compatible fiber is key in making semiconductors. It stops outgassing, which can ruin sensitive equipment. This fiber keeps the vacuum chamber clean.
Big companies like Applied Materials use it. It’s vital for keeping semiconductors free from contamination.
How do metal coatings improve electrical conductivity in fiber applications?
Metal coatings turn non-conductive fibers into conductive paths. They make the fiber core conductive. This is useful for controlling static and shielding against electromagnetic interference.
The coating is all around the fiber, making it easy to use. It’s not like carbon fiber, which is directional.
What maintenance is required for metal coated fiber installations?
Regular checks are needed to keep the fiber in good shape. Look for signs of wear or damage. Check the resistance to spot any issues early.
Make sure the fiber is supported right. This prevents damage from weight or movement. Inspect the connections for any stress.
Most need checks every few months and a full test once a year.
Are metal coated fibers cost-effective compared to traditional solutions?
Metal coated fibers cost more upfront but save money in the long run. They last longer and need less maintenance. This is important in places where failure can be very expensive.
For example, in vacuum chambers, a small problem can cost millions. The extra cost of metal coated fibers is worth it to avoid these problems.
What innovations are driving the future of metal coating technologies?
New coating methods ensure the coating is just the right thickness. This makes the fibers work better. Companies like Veeco Instruments are making these fibers even better.
New coatings combine different metals for better performance. This makes the fibers more affordable for use in new technologies. They’re being used in renewable energy and aerospace.