Medical fiber technology has changed healthcare a lot. It allows for precise treatments and tests. The market for medical laser fibers grew to $1.25 billion in 2024. It’s expected to reach $2.68 billion by 2032, growing 10.05% every year.
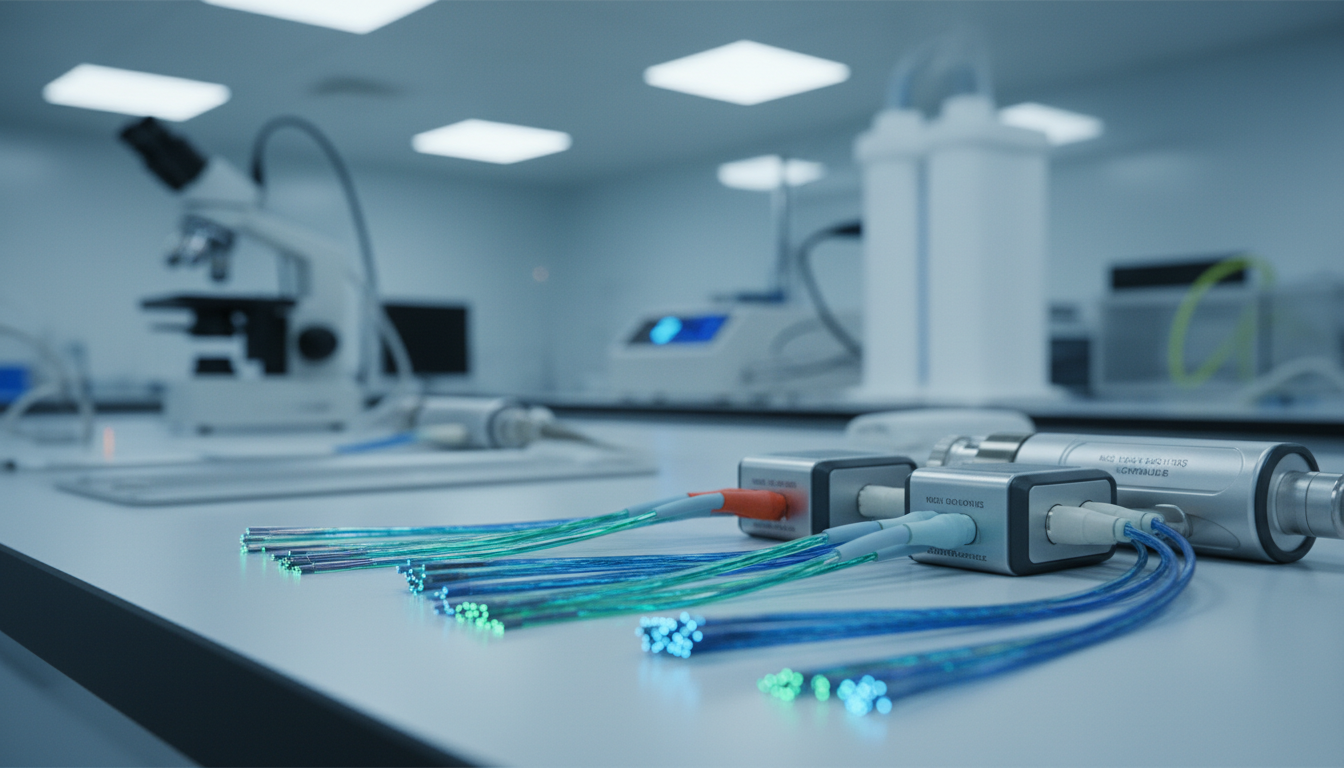
Medical optical fiber is made of special glass threads. They send laser energy through the body with great accuracy. Companies like WEINERT Fiber Optics make NeuLight BareFibers in ISO13485 certified places for safety. These fibers work from 500 to 2200 nanometers and can handle up to 100 watts.
The core of medical fiber is made of fused silica. It’s surrounded by doped silica cladding in a four-layer design. For healthcare, the core sizes vary from 200 to 940 micrometers. Each fiber has an SMA-905 connector and comes in sterile packaging for hospitals.
Fiber optic technology in medicine does more than just send light. It helps surgeons remove tumors and clear blocked arteries. It also makes minimally invasive procedures possible. The choice of materials and strict standards make medical optical fiber safe for use inside the body.
Key Takeaways
- Medical fiber market will double from $1.25 billion to $2.68 billion between 2024 and 2032
- Fused silica cores with specialized cladding create safe pathways for laser energy
- Core sizes range from 200 to 940 micrometers for different medical procedures
- ISO13485 certification ensures manufacturing meets healthcare safety requirements
- Wavelength range of 500-2200nm covers most surgical and diagnostic needs
- Power delivery up to 100 watts enables both gentle and powerful treatments
What is Medical Fiber and Its Importance?
Medical fibers are special optical paths that carry laser energy to specific areas inside the body. These biocompatible fiber systems have changed healthcare a lot. They allow for precise energy delivery during treatments.
Doctors use these advanced tools for precise procedures. This makes their work more accurate.
The role of surgical fibers is huge in many medical fields. They help in urology, oncology, dermatology, and ophthalmology. Thanks to them, patients face smaller cuts, less pain, and quicker recovery times.
These fibers make minimally invasive procedures possible. This is a big deal for patients.
Some key uses include:
- Kidney stone removal through lithotripsy
- Prostate treatments for benign enlargement
- Tumor ablation in cancer therapy
- Skin resurfacing and aesthetic procedures
- Eye surgeries for vision correction
Laser therapy through medical fibers has big benefits. It’s precise, which means less harm to healthy tissues. This leads to better results and fewer complications for patients.
The need for minimally invasive procedures is growing. This is because more people have chronic conditions like kidney stones and skin issues. Doctors are using these advanced tools more and more. They offer safety, efficiency, and comfort to patients.
Composition of Medical Grade Optical Fiber
Medical grade optical fibers need careful material choice for safety and performance. The core of ISO medical fiber is made of fused silica, a pure glass. It transmits light well, helping doctors use lasers and see clearly during surgeries.
The fiber has key layers. At the heart, fused silica makes up the core, with sizes from 200 to 940 micrometers. Around it, doped silica cladding acts as a shield, guiding light. Its size, from 240 to 1000 micrometers, is vital for medical use.
Choosing materials focuses on biocompatible materials that pass strict tests. Each part must not break down when faced with body fluids or sterilization. The outer layers use polymers and metals that stay strong, even in changing medical conditions.
Top medical fibers keep signal strength high, which is key for precise work or detailed images. The making of fused silica cores and doped silica cladding cuts down on light loss. This ensures the fiber works well in critical medical situations. These materials are tested hard to prove they’re safe for patients and reliable in hospitals.
Design Features of Medical Optical Fiber
The engineering of medical optical fiber is all about precision and safety. It meets the high standards of surgery. Each fiber has a four-layer silica structure for reliable performance in critical procedures.
This design lets surgeons work confidently. They know their tools can handle intense tasks.
Power handling depends on the fiber’s core diameter. Smaller cores manage 20 to 40 watts, while larger ones can handle up to 100 watts. These fibers deliver 1.5 to 4 joules per pulse. They’re perfect for delicate eye surgeries and strong tissue ablation.
The design includes flexible tips for different needs. Flat tips are great for precise cuts, and rounded tips are better for gentle coagulation. Hospitals choose between disposable fibers for cleanliness or reusable ones for cost savings.
Advanced coatings protect the fiber and boost light transmission. These coatings help the fiber last longer and work well after being sterilized many times. The fibers work in the visible and near-infrared spectrum, from 0.5 to 2.2 micrometers.
Some fibers are as small as 200 microns. They allow for tiny incisions in surgery. This approach cuts down on recovery time and scarring, keeping precision high.
Safety Standards for Medical Fibers
Medical fibers must meet strict safety standards before they reach hospitals and clinics. The FDA has very detailed rules for optical fibers used in medical procedures. Every ISO medical fiber is tested thoroughly to ensure it’s safe for patients.
Manufacturing facilities need ISO13485 certification to make these special fibers. This shows they follow international quality management systems for medical devices. They go through regular audits to keep their certification.
- Biocompatibility testing for all materials touching patients
- Sterilization compatibility for reusable fiber systems
- Environmental protection against heat and vibration
- Sealed enclosures preventing dust and water damage
Single-use fibers are now common in many procedures. They help avoid cross-contamination between patients. This approach significantly reduces infection rates in sensitive surgical environments.
FDA standards require strict testing protocols. Each batch of ISO medical fiber is checked for optical performance, mechanical strength, and chemical stability. Medical device regulations also demand detailed documentation of every production step.
Patient safety drives the constant improvement in fiber design. New barrier coatings protect internal optics from bodily fluids. Advanced materials also resist degradation during repeated sterilization cycles. These advancements come from ISO13485 certified manufacturers’ heavy investment in research and development.
Manufacturing Processes of Medical Fiber
Teams in Europe and the United States make biocompatible fiber in special facilities. These places are ISO 13485-certified, ensuring products meet high healthcare standards. They aim to make fiber production efficient and affordable, helping more hospitals and clinics get advanced tools.
Modern fiber production uses automated systems for consistent results. Robots place components with great accuracy, thanks to optical feedback. This automation speeds up production, cuts costs, and makes products more reliable. Each fiber is checked multiple times during assembly.
Quality control begins with careful mechanical design. Engineers use special bearings and mounting systems for stability. Self-centering mechanisms ensure light travels straight through the fiber, even when it’s moving.
Real-time monitoring tracks each fiber’s performance. Sensors catch small changes in light transmission early. This alerts technicians to perform maintenance, preventing failures during important procedures. Smart systems record data to help improve production methods.
Cost-effective manufacturing makes these tools available globally. By streamlining production without losing safety or performance, manufacturers help doctors use the latest technology for patient care.
Innovative Uses of Medical Grade Optical Fiber
Medical fiber technology has changed patient care in big ways. Smart fibers now have sensors to track temperature and tissue interaction during surgery. This lets doctors see real-time data during delicate operations.
Multi-wavelength fibers meet different needs in various specialties. In urology, they help remove kidney stones with precision. Oncology uses them for tumor removal with less damage to nearby tissue. Aesthetic clinics use them for skin treatments and hair removal.
Robotics-assisted systems now use hollow core fibers for better power delivery. This leads to more precise and controlled laser procedures. Telemedicine lets remote specialists guide local surgeons in complex fiber-optic surgeries.
| Medical Specialty | Fiber Application | Clinical Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Urology | Lithotripsy fibers | 95% stone fragmentation rate |
| Oncology | Ablation fibers | Reduced recovery time by 60% |
| Dermatology | Aesthetic laser fibers | Minimal scarring risk |
| General Surgery | Cutting fibers | 40% less blood loss |
Advanced imaging now works with fiber systems for guided surgeries. Surgeons can choose fiber types based on their needs. This makes medical fiber key for modern healthcare in many fields.
Comparison with Other Medical Technologies
Medical optical fiber is different from old surgical methods. Patients usually spend less time in the hospital. They recover faster and face fewer risks than with traditional surgery.
The laser advantages in minimally invasive surgery also help hospitals. They see benefits like:
- Disposable fibers that cut down on cleaning and sterilizing costs
- Reusable fibers that last longer and need to be replaced less often
- Precision targeting that saves healthy tissue during surgery
- Less need for general anesthesia in many cases
Medical optical fiber works well and efficiently. It has low insertion loss, from 0.5 to 3 dB per channel. This depends on the application. Multi-channel systems might see a bit more signal loss, but they’re more precise than many other tools.
Starting to use this technology costs money. You need to buy equipment and train staff. But, the long-term savings are worth it. Hospitals save money because procedures are shorter, there are fewer complications, and patients stay in the hospital less.
More doctors are moving to minimally invasive surgery. Medical optical fiber is leading this change. It offers benefits that older tools can’t match.
Future Trends in Medical Fiber Technology

The medical fiber industry is on the brink of a revolution. New technologies are set to change patient care in big ways. Experts say the growth rate will be 10.05% every year until 2032.
Several major breakthroughs are changing the medical field:
- Biodegradable fibers for temporary treatments that break down on their own
- Nanotechnology that makes fibers target cells more precisely
- Miniaturization that lets us reach parts of the body we couldn’t before
- Optical gels that reduce light reflection for clearer images
- Systems that speed up data transmission by a lot
The Asia Pacific is leading this change with a 11.5% growth rate. Big names like Lumenis Be Ltd., Boston Scientific Corporation, and Olympus Corporation are pouring money into research. They know that today’s tech is tomorrow’s care.
New uses for ISO medical fiber include monitoring diseases in real-time and delivering drugs exactly where needed. These advancements mean patients can recover faster and get better results. As we keep pushing the limits of what’s possible, fiber optic tech will be key in making healthcare more precise and personal.
Conclusion: The Future of Medical Fiber in Healthcare
The medical fiber market is on the verge of a big change. It’s expected to grow from USD 1.25 billion to USD 2.68 billion by 2032. This growth shows how doctors are using biocompatible fiber for more precise treatments.
Outpatient laser procedures are becoming more common. This is creating a strong need for disposable fibers that are safe. These fibers must meet strict safety standards.
Several factors are changing healthcare with medical fiber at the forefront. The aging population needs more treatments that don’t involve big surgeries. Countries like India and Brazil are improving their healthcare systems, opening new markets for biocompatible fiber products.
Companies like Boston Scientific and Olympus Corporation are investing in research. They aim to make fibers that work better and cost less. This will help patients in the future.
Environmental concerns are also driving the industry to be greener. Manufacturers are now using sustainable materials. They want to keep quality high while being eco-friendly.
There are investment opportunities in every part of the supply chain. From raw material suppliers to makers of specialized equipment. As medical fiber technology improves, patients will see safer procedures and faster recovery times.
FAQ
What makes a fiber “medical grade” and biocompatible?
Medical grade fibers are made in ISO13485 certified places. They go through a lot of testing to make sure they’re safe for patients. These fibers have materials like fused silica cores and doped silica cladding that meet strict rules.
They’re made to prevent bad reactions in surgeries. You can find them in both sterile single-use and reusable forms. These forms stay good after being sterilized.
What are the standard core sizes available for medical optical fibers?
Medical optical fibers come in many core sizes for different uses. The NeuLight BareFibers from WEINERT Fiber Optics have sizes like 200um, 273um, and 365um. They also have sizes of 400um, 550um, 600um, 800um, and 940um.
Each size is made for specific tasks. Smaller sizes (200-400um) are for very precise, small surgeries. Bigger cores (600-940um) can handle up to 100W for bigger surgeries.
How much power can medical laser fibers safely deliver?
The power a medical fiber can handle depends on its size and design. These fibers can take up to 100W of power. They can also handle up to 4J of energy.
The 4-layer all silica fiber structure keeps power safe during surgeries. New coatings help these fibers handle more power and last longer. They work well in the 500nm to 2200nm wavelength range.
What’s the difference between disposable and reusable medical fibers?
Disposable medical fibers are great because they don’t spread germs and save on cleaning costs. They come ready to use in sterile packaging. Reusable fibers need to be cleaned and sterilized but are cheaper in the long run.
Both types have the same quality and are available in different tip shapes. This depends on what the doctor needs.
Which medical procedures commonly use laser fibers?
Laser fibers are used in many areas of medicine. They help break up kidney stones in lithotripsy and treat prostate issues in urology. They’re also used in cancer treatments and for skin care.
General surgery, dermatology, and eye treatments also use them. They’re good for cutting, coagulating, and removing tissue through small openings.
What ISO standards apply to medical fiber manufacturing?
ISO13485 is the main standard for making medical fibers. It makes sure the quality management system for medical devices is followed. This includes everything from picking materials to packaging the fibers.
Places in Europe and the United States follow these rules. They have strict quality checks, tests for safety, and need to keep detailed records. This ensures the fibers are always safe and work well.
How do medical fibers compare cost-wise to traditional surgical methods?
Medical fibers might cost more at first, but they save money in the long run. They help patients recover faster and have fewer problems than old surgery methods. This makes them a good choice for many doctors.
The market for these fibers is growing fast. It’s expected to be worth USD 2.68 billion by 2032. This shows more doctors are choosing them for their benefits.
What future developments are expected in medical fiber technology?
Medical fiber technology is getting smarter. New fibers have sensors to check temperature and tissue in real-time. There are also fibers that can dissolve on their own for temporary treatments.
There are fibers that can carry more power too. These changes will help doctors reach smaller areas and treat more problems. They’ll also be able to use different colors for more treatments.